Difference between revisions of "GitLab server"
| Line 207: | Line 207: | ||
The command above will important all new files and existing files that have been updated. | The command above will important all new files and existing files that have been updated. | ||
| − | === | + | === Working as a team === |
Once all developers have a local copy of your repository, it's a case of simple pulling and pushing changes to and from the central repository. | Once all developers have a local copy of your repository, it's a case of simple pulling and pushing changes to and from the central repository. | ||
Revision as of 13:52, 16 February 2015
GitLab server
The University provides every student with a fully working Version Control system called GitLab:
Please note that you should only use this server to store files related to University coursework. Personal or word related files should not be stored on this server.
Signing in
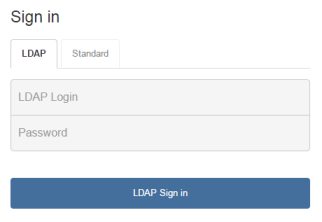
You can sign in using your usual university credentials. Make sure that you select the "LDAP" tab on the "Sign in" screen:
Creating a project
Your next step is to create a "Project" that will contain your work. Click on the "+ New Project" button.

And populate the following fields:
- Project Name
- Description
- Visibility Level
Important: The Visibility Level should be set to "Private" for all assessment-related work. Any other Visibility Level would allow other students to look at and clone your work, which equates to Collusion under the University's Academic Misconduct regulations.
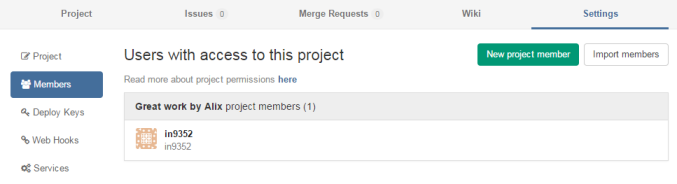
Set the Project's Visibility level to "Private" and then manually invite new project members, via the Project's settings:
Creating your first repository
When visiting your project's homepage you are presented with some Git commands that you should run to create your first repository. Please note that you get 2 access options:
- SSH
- HTTPS
We'll look that HTTPS for now, so click on the "HTTPS" button near the top.
Git commands
Your project's homepage should contain commands similars to these ones (actual details will vary):
Git global setup
git config --global user.name "in9352" git config --global user.email "alix.bergeret@wlv.ac.uk"
Create a new repository
mkdir great-work-by-alix cd great-work-by-alix git init touch README.md git add README.md git commit -m "first commit" git remote add origin git@fsegitlab.wlv.ac.uk:in9352/great-work-by-alix.git git push -u origin master
Push an existing Git repository
cd existing_git_repo git remote add origin https://fsegitlab.wlv.ac.uk/in9352/great-work-by-alix.git git push -u origin master
In order to run the code above you have 3 options:
- [Windows] Run "Git Bash", a Git client installed in all MI labs
- [Windows] SSH into mi-linux.wlv.ac.uk using an SSH client such as Putty
- [Linux] Boot under Linux, and open a Command window.
Git commands - details
Let's look at each command in more details:
git config --global user.name "in9352" git config --global user.email "alix.bergeret@wlv.ac.uk"
The commands above simply set some global settings (your user name and email address) that are required for this process.
If you omit these you will get the following warning later on:
- "Your name and email address were configured automatically based on your username and hostname. Please check that they are accurate. You can suppress this message by setting them explicitly."
mkdir great-work-by-alix cd great-work-by-alix
Well, nothing too difficult here, we simply create an empty folder and move into it. Note that you may wish to move into an existing folder that already contains files instead!
git init
Here is the first important command. git init creates an empty Git repository (on your local system). If the command is successful you should get a message stating "Initialized empty Git repository in ...". This has created a hidden ".git" folder that you can see by running the command "ls -la".
touch README.md
This command simply creates an empty test file called "README.md". If you already have files in your folder (e.g. PHP files), then you don't need to do this.
git add README.md
Second important command. git add adds a file to the repository's index. We can run this command to add our dummy "README.md" file, or any existing files you may have.
git commit -m "first commit"
Third important command! git commit records all changes to the local repository. This should be run regularly when your code is in a working, stable state. Important: for now your changes were only committing to the local repository. To commit them to the central repository you'll need the "push" command below.
Important: It is always considered good practice to type in a comment when committing code to a repository, so that other developers can read about your update. When using the command line this is done using the -m argument, as demonstrated above.
git remote add origin https://fsegitlab.wlv.ac.uk/in9352/great-work-by-alix.git
This is an optional command that create a "remote", aka an alias (or shortcut) to your lengthy repository's full address. In this case we name it "origin". So from now on we can simply refer to "origin" when working with this repository (see below!)
Note: your repository's address should contain "https://". If it doesn't then your forgot to press the "HTTPS" button earlier.
git push -u origin master
And here is the final important command! git push commits all local changes to the central repository, i.e. "origin", definied in the previous step.
The second parameter is the "branch" you want to commit to. In this case we create a default branch called "master". We'll worry about branches later.
Important: for now you will need to retype your login and password every time you want to push changes to the central repository. We'll get around this later using the SHH method instead of HTTPS.
Has it worked?
If you go back to GitLab (in your browser) and refresh your project's homepage you should now see something similar to this:
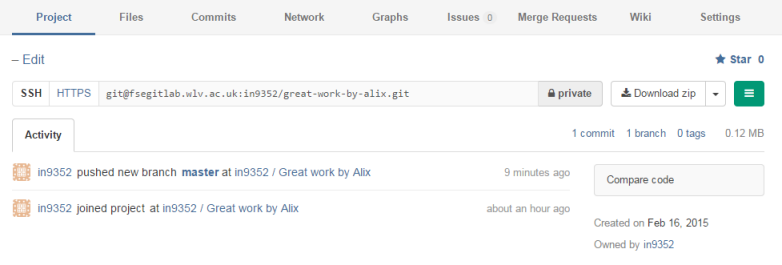
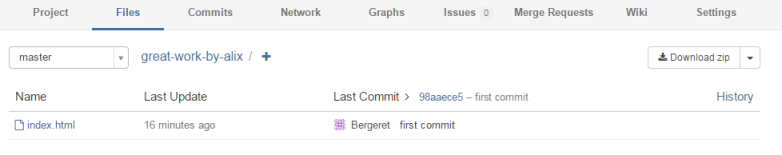
We can see 1 commit to our new branch "master". If you click on the "Files" tab at the top you will see the files you pushed earlier. In my case I pushed a file called "index.html":
Summary of important commands
Whether you use an old fashion command line Git Client or a fancy IDE, it is crucial to understand the process and the various steps required when working with git:
- git init: Creates an empty Git repository
- git add: Adds a file to the repository's index
- git commit: Commits changes to local repository
- git push: Commits changes to remote repository
Importing from repository
So far we have explained how to commit (i.e. push) changes from your local repository to the central repository. But what about the other way around? There are 2 git commands for this:
- git-pull: Pulls a copy of a project from Git repository server to the local file system and synchronize between the two. Note that in order to pull (or push) a project, you must have either created the project (e.g., using the git init command), or cloned the project (e.g., using the git clone command, see below).
- git-clone: Creates a copy of a project on your local file system. You can use this command to "import" a project from Gitlab that was not originally created by you (e.g., by your teammates.)
Cloning
If other team members wishes to work on the repository you created earlier then they will need to "clone" it first:
git clone https://fsegitlab.wlv.ac.uk/in9352/great-work-by-alix.git
The command above:
- creates a new folder
- creates the local repository
- imports all the files from the server to the local repository
You are essentially create a duplicate working copy of the project.
You might make a change to an existing file, or even add new files:
gedit index.html // make a change to the file and save touch page2.html git add page2.htm git commit -m "Commit by team member" git push -u origin master
The commands above allow you to:
- make a change to the existing "index.html" file
- create a new "page2.html" file (empty for now) and commit it locally
- push all changes back to the server
Pulling
If you already have a local copy of a repository (you either created it in the first place, or cloned it earlier), and only need to "pull" the latest changes from your team, then you'll need the "git pull" command:
git pull origin
Note: we are reusing the alias we created earlier ("origin"), which is a shortcut for our repository's URL.
The command above will important all new files and existing files that have been updated.
Working as a team
Once all developers have a local copy of your repository, it's a case of simple pulling and pushing changes to and from the central repository.